Around 4,000 years ago, there was a bustling and prosperous city that became one of the most prominent and innovative cities in the world. Its streets were skillfully paved and boasted several gates that provided entry into the walled city. The towering city walls were adorned with over 250 towers, each standing at a towering height of at least 100 meters. This city was the birthplace of modern mathematics and writing, which revolutionized the world forever.
The city’s transportation system was remarkable, with ferries, roads, and drawbridges making it efficient and accessible. The legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the ancient world, were an astonishing engineering feat that left the world in awe.
The wealth of Babylon was beyond imagination, and the city’s artisans created magnificent works of art using gold. Among these works were a golden image of Baal, a stunning table that reputedly consisted of 22,000 kilos of pure gold, a golden lion, and a golden statue of a man. The royal palace was a majestic sight to behold, and it was the most massive ever built in the history of the world.
Babylon was located in what is now known as Iraq. Almost everyone has heard of Babylon, or at the very least, the Tower of Babel, which was the tallest structure in the world at that time. However, how did this city rise to such unprecedented heights and experience a catastrophic fall?
Rise of the Amorites
The birth of Babylon occurred after the fall of the Akkadian Empire. Two new empires popped up and began to claim the nearby land. The Babylonians were in the south, and the Assyrians were in the north. The Babylonians would be the first group of people to create an empire that would claim the entire country of Mesopotamia. The city-state of Babylon had been in Mesopotamia for years, but things were now beginning to look up for Babylon as it seemed they had claimed the majority of the land for themselves.
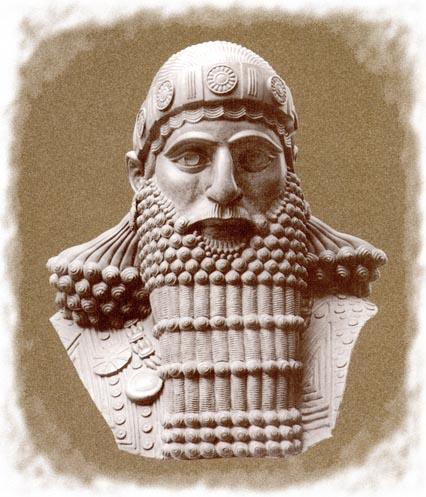

When the Akkadian Empire began to fall, the Amorites moved in to claim their territory. This all took place sometime around 1792 BC when King Hammurabi was elected ruler. It wouldn’t be long after Hammurabi became king that he would want to expand his reach. He loved his job, but he felt as though he should be able to rule over much more than just Babylon. This led him to his desire to conquer other city-states in the area, doing his best to claim control of all the nearby settlements. Within a few short years, he had been able to successfully conquer the entire country of Mesopotamia, including the Assyrians in the north.
Babylon’s Prosperity and Riches
Because of Hammurabi’s unwillingness to back down, he would become one of the most powerful rulers of his time and helped Babylon become the richest and most prosperous city in ancient history. Much of Babylon was located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The city served as a major trading area for people from all over the world. Supplies and goods were abundant, so the city saw a constant flow of money, services, and resources. The city was also highly advanced and would be the first to adopt all the new ideas and products that were being invented across the globe at the time. Babylon was also by far the largest city in the world. It’s estimated that as many as 200,000 people lived in Babylon at its peak.
In the center of the city, the locals had built a large pyramid that they used as a temple. Researchers believed that this pyramid would have been around 100 meters tall, with wide streets that would lead to it from all the city entrances. Around the pyramids and other areas of the city would have been gardens, palaces, towers, and beautiful works of art that were unlike anything humans had ever seen. The city was also the cultural epicenter of the world, with science, music, mathematics, astronomy, and literature thriving within its walls.
The invention of writing and mathematics is something we take for granted these days. They helped spur a movement that would create various forms of writing and normalize writing as a way of taking notes and documenting history and other facts that have since been lost to time. They also claim to have invented the wheel, modern agriculture, the bow, the plow, irrigation, and several other inventions that helped found humanity as we know it. Without the Babylonians and their various inventions, we would not be who we are today. But did you know that many of the people who originally invented these machines, such as the wheel or the plow, claim that the ideas were given to them by angels or aliens? We don’t know too much about the invention of most of these things, but many early humans claimed to have been visited by beings that descended from the sky and informed them how to live a prosperous life and use their surrounding resources to their advantage. It’s super interesting stuff, but we’re getting a little off-topic. Anyway, the Babylonians helped invent the first form of a writing system that involved clay tablets that would be engraved with wedge-shaped letters. This helped document much of their history and how they created early mathematics. To put this into perspective, these writing methods allow us to know more about ancient Babylon than we know about ancient Egypt.

The Babylonians would also invent the fundamentals of modern mathematics. They would be the first civilization to use mathematics to help measure land, tax people, and conduct all sorts of business. They would also use numbers to document the night sky so they could create a lunar calendar that was shockingly accurate for its time. They were also the first civilization to use symbols to represent large numbers. For example, if a person needed to document that they owned 50 bales of wheat, they would have originally had to draw 50 individual symbols to represent this. However, as they became more efficient with their writing, they created symbols to represent numbers like 1, 10, and 60. We also have reason to believe that the Babylonians developed the first abacus, which is essentially an early version of a calculator.
Hammurabi’s Code
Written law, or the Hammurabi Code: It may shock you to know that King Hammurabi was the first person to ever request that laws be written down. That seems pretty weird, right? Well, before this moment, most of the laws were just passed around by word of mouth, or they were implied. As you may expect, this left a lot of legal gray area for citizens, as they had no way to know for sure what was right or wrong. For example, John may tell you that it’s illegal to own more than 50 piles of wheat. If you own more than that, you’re supposed to give it away to the person closest to you. So John runs off with half your crop of wheat. Little did you know, John was lying. John robbed you. Okay, obviously, that’s a bit of a ridiculous way to think about it.
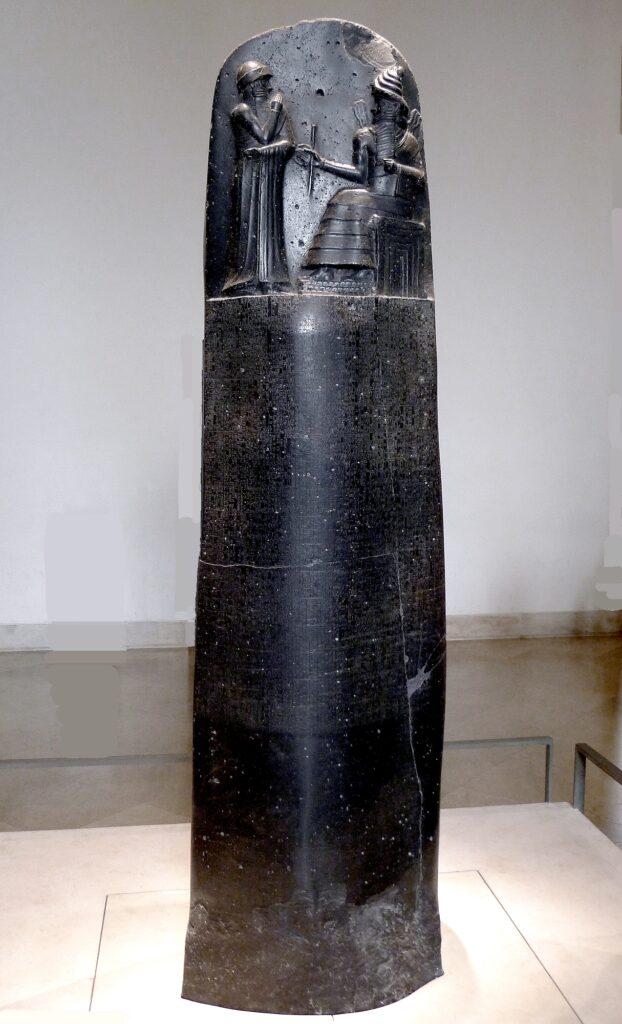

But before Hammurabi decided to write down the laws, there was no surefire way to know what the king would consider illegal. Hammurabi asked some of his workers to create giant pillars that would list the various laws of the land. At the time, there were just 282 laws, much different from today’s world when there are thousands of laws we have to abide by. Most of Hammurabi’s laws were strangely specific, but these rules would serve as guidelines that could be used if similar circumstances were to occur. For example, what you should legally do if your neighbor convinces you to give him all of your wheat. There were tons of laws that would help regulate businesses, make sure you paid your workers their wages, rules for trading, rental prices, slave prices, and the list goes on and on. There were also the obvious laws that would dictate what would be considered criminal behavior and what would happen to you if you were caught breaking the law. There were even laws about adoption, marriage, and divorce.
So what caused this incredible city to eventually crumble and nearly be lost to time?
Babylon’s declining strength and loss of faith
After Hammurabi’s death, his sons inherited the task of governing the city. However, they lacked their father’s resolute nature and leadership abilities. As a result, Babylon’s strength slowly declined, and neighboring regions began to lose faith in the city. Observing the weakening state of Babylon, the Kassites invaded and conquered it, toppling the new rulers and seizing control for themselves. This occupation lasted for roughly four centuries, during which time the Kassites overturned Hammurabi’s laws and transformed the city to suit their own purposes.
Later, the Assyrians would overtake the Kassites and claim Babylon as their own. Eventually, in 612 BC, the Babylonians were able to reclaim the city, establishing the Neo-Babylonian empire, the second Babylonian empire. This occurred with the help of King Nabopolassar, who took advantage of the downfall of the Assyrian empire and claimed the throne for himself. His son, King Nebuchadnezzar II, proved to be an exceptional leader and military strategist, ruling with a firm hand and earning the respect of the citizens. Under his reign, Babylon expanded westward and acquired more territory.
However, the Hebrews were captured and enslaved for 70 years during Nebuchadnezzar’s reign, as told in several accounts in the Bible. After Nebuchadnezzar’s death, the city once again began to falter and decline.

By 529 BC, the city had been claimed by the Persians and was now listed as part of the Persian Empire. Everything Nebuchadnezzar had done to restore the city had once again been undone.
The Tower of Babel, one of the most incredible things to come out of Babylon, was the invention of the infamous Tower of Babel that is mentioned in the Bible and proven by history. This building was constructed shortly after the Great Flood, which wiped out nearly everything and everyone on the planet. According to biblical accounts, the Tower of Babel was built when all of the inhabitants of Mesopotamia still spoke the same language when they settled in the area. They wanted to build a large tower that would reach the sky. Some people seem to believe that the locals built the tower so that they could eventually reach heaven, though others believe that they built the tower so that they would not be drowned by another Great Flood.

Either way, biblical accounts say that God had other plans. He confused the people by forcing them to forget their native tongue and speak new languages. They were no longer able to communicate, so the construction of the tower quickly fell apart. We don’t know for sure which structure in the area is the aforementioned Tower of Babel, but researchers tend to believe that the best candidate is the Etemenanki of Babylon. This tower was allegedly dedicated to Marduk, the patron god of Babylon. Since several temples like this have been found in the area, it would make sense that a building like this could have been used as the basis for the Tower of Babel.
Babylon today, under the rule of Saddam Hussein, the Iraqi government led a mission to excavate Babylon and attempt to bring the city back to life, including rebuilding and reconstructing one of Nebuchadnezzar’s palaces. However, after the United States invaded Iraq back in 2003, their plans completely fell apart. The area was eventually reopened to tourists in 2009, though the project was never completed.
Thanks to the Babylonians inventing modern writing, we know so much about their city and how humans once lived. If only this were true for other parts of the world, history may tell a much different story.