There are very few powerful nations that have not contemplated the idea of capturing Afghanistan. However, none of them have been successful in doing so. This begs the question: why have these superpowers failed in their attempts? Additionally, what compelled the USA to send Osama bin Laden to Afghanistan, only for him to later become a significant problem for them?
Despite its lack of abundant resources, Afghanistan has attracted the attention of both Russia and the USA, who have invested millions of dollars in their attempts to capture it. Yet, time and time again, they have returned empty-handed. In this article, we will delve into these issues in detail. But first, let us take a look at the historical context.
All these things started in 1839 when both the British and Russian empires were increasing their influence on Afghanistan. Because Afghanistan’s location in South Asia is very important and strategic, the hassle of the British and Russian empires for Afghanistan was called the Great Game.
The situation in Afghanistan had escalated to the point that, without much consideration, the British sent an army of 16,500 soldiers, who were mostly killed by Afghan forces except for a few British soldiers.
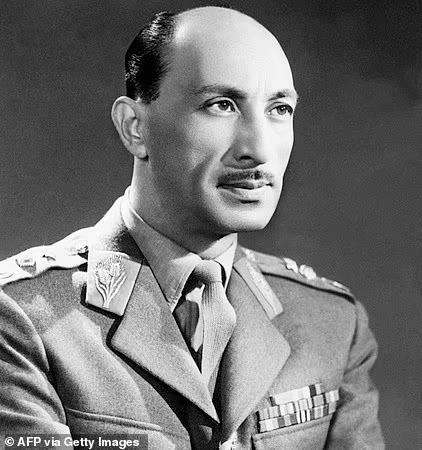

In 1933, Zahir Shah became the last king of Afghanistan. And this was the time, when Afghanistan was a bit stable. He introduced modernization in Afghanistan. When the neighbouring countries started having Democracy, so he too implemented the first constitution of Afghanistan in 1964. In which, a parliament with two houses was established. And a cousin of Zahir Shah, Daoud Khan, who he trusted very much, made him the prime minister. Now implementing a constitution, making parliament houses, Zahir Shah was doing all these, but he kept all the power. Only that happens which Zahir Shah has said, and although people silently protested, they could not speak out.
Ending of Kingship regime
In 1973, Zahir Shah’s health took a turn for the worse, and until then, there was not much development in Afghanistan, so he had to go to Italy for treatment. On July 17, 1973 during his absence, his trusted cousin, Daoud Khan, seized power, and both the army and the people of Afghanistan supported him. The common people of Afghanistan wanted that kingship gets over and democracy starts. So that people get power, because even they were fed up of kingship, that’s why they did not go against Daoud much.
Now Zahir Shah gets to know this in Italy, that Afghanistan is toppled.. And if he goes back, he would be murdered. That’s why he takes exile in Italy, and stays there. After that, Daoud Khan makes himself the president of Afghanistan and implemented democracy. But here, he makes a mistake. He does implement democracy, but puts a condition, that only his party could participate in the elections. And this made the common people of Afghanistan feel cheated, that this is the same thing.And with that, after some time, things become expensive and Poverty increases in Afghanistan. Due to which people get more fed up. And not just that, along that, Daoud was constructing only in big cities, and completely ignored the smaller districts were ignored. Now the population of smaller districts, got angry towards this thing. They thought even Zahir Shah was better than this. Seeing all these things and getting fed up of Daoud Khan, many groups of Afghanistan create a party, People’s democratic party of Afghanistan, PDPA.
During this political turnmoil, the People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA), a communist party influenced by the USSR, gained popularity. The PDPA was supported by Russia, and when the economic conditions worsened, the party became more powerful, which led to Daoud Khan’s attempts to suppress the party. And a very big leader of PDPA, Mir Akbar Khyber was murdered by him. PDPA party’s people started to be sent to jails. However, this only made things worse, as PDPA gained the support of the government’s military officers. And after that, 27th of April 1978 comes, on this date, Daoud Khan and his family was killed, again toppling happens, and PDPA gains control in Afghanistan. Nur Muhammad Taraki became the new president, who was favored by the USSR due to his strong communist beliefs. Just as communist did not believe in a god, so even Nur propagated that ideology. The changes brought by Nur Muhammad were significant for Afghanistan.
Failed attempt to bring Modernization in Afghanistan
Afghanistan is a Muslim country where Nur initiated modernization and secularism. Females were allowed to receive education, dress fashionably, drive cars and move about freely. Nur made education compulsory and eliminated religious education from the syllabus. He raised the minimum age of marriage, banned forced marriage, and aimed to improve women’s participation in politics and the workforce. He limited the influence of religious leaders and stopped public displays of religion. Nur did not stop there; he brought about land reform under the influence of the USSR. This resulted in those with more land giving to those with less and the forgiveness of debts for agriculture to promote equality.

As a result, opponents of Nur’s government claimed that it was challenging traditional Afghan values and that they were being influenced by the USSR. The traditional and religious landowners, in particular, began to oppose the government, which responded with suppression. This led to fighting between the government and people in various parts of Afghanistan. This fight started to be called that this fight is to protect Islam and those small groups who were fighting against government in different areas, were collectively called Mujahideen. With these Mujahideens, some tribal leaders and military people also joined. These groups were not only led by Islamic scholars, but also by local leaders and students. The common aim of all the groups was to topple the PDPA communist government led by Nur Muhammad Tariki as the PM and Hafizullah Amin as the Foreign Minister/Deputy PM.
However, the USSR found Amin to be unreliable and suspected that he was an agent of the US CIA. On 20 March 1979, Nur went to Moscow where the USSR informed him that Amin was working with the CIA. They advised him to remove Amin from his ministry and reduce social reforms in Afghanistan. Nur agreed to their requests and informed Amin about his removal. However, Amin learned about the plan from the CIA and killed Nur and his family at the airport upon his return. Amin became PM himself, but the USSR saw this as a direct challenge to them and decided to take control of Afghanistan.
Upon learning of these events, the Soviet Union quickly realized that it was losing its grip on Afghanistan. The Mujahideen rebelled against the communist government in various regions, while some factions remained loyal and were subsequently eliminated.
This was not merely a matter of murder, but a direct challenge to Soviet authority. To make matters worse, the newly installed leader of Afghanistan was supported by the United States, leaving no doubt that the country would now be aligned with American interests.
Given these circumstances, it was inevitable that Afghanistan would fall under US control. As a result, on December 24th, 1979, the Soviet Union dispatched thousands of troops to Kabul to take control of the government and military apparatus.
During this operation, the Soviet forces eliminated Afghan leader Amin and appointed Babrak Kamal as a puppet leader. With this move, the USSR regained control over significant portions of Afghanistan.
US Weaponized Religion to Defeat the USSR in Afghanistan
When the world criticized the USSR for its actions in Afghanistan, the USSR claimed that it was helping the Afghan government deal with extremists and not attacking the country. However, the Afghan people were infuriated by this and a growing number of individuals became Mujahideens, seeking revenge against the USSR. The US had also put a lot of effort into the region, so it was not happy with the situation either.
As a result, US President Jimmy Carter declared that Afghanistan’s actions in the US Persian Gulf region posed a threat to the US. Therefore, the US would take any necessary action, even if it meant using military force, to protect its interests. Consequently, the US had only two allies in Asia at that time, Pakistan and Saudi Arabia. If the USSR had gained influence in Afghanistan, it would have been unable to expand its power throughout the entire region. This made it crucial for the US to have influence in Afghanistan.
If the US had directly intervened in Afghanistan, a direct war between the US and the USSR would have been inevitable. The US opted for a different strategy, turning many Islamic countries against the USSR by depicting their actions as an attack on religion. The US supported the Mujahideens, who were fighting inside Afghanistan, in every way possible. After consulting with Pakistan, the US began training the Mujahideens in Pakistan, which resulted in Pakistan receiving a significant amount of money.
In addition, the US sought assistance from Saudi Arabia in the region. The CIA and the Pakistan ISI established the Maktab al Khidamat organization and urged people in the region to participate in the fight. Several individuals, including Osama bin Laden, Abdullah Azzam, and Omar Khadr, played a crucial role in providing financial support and developing strategies on a grand scale. They monitored all of the recruitment activities of the Mujahideens in the area, which eventually led to the creation of Al Qaeda.
Western countries also supported the US in this endeavor. In films of that time, such as the 1986 James Bond film “The Living Daylights” and the 1988 movie “Rambo,” the Mujahideens were depicted as courageous fighters, which aimed to influence the younger generation. Despite the USSR’s powerful army, the terrain and extreme weather in Afghanistan presented significant challenges for them. The Mujahideens would launch guerrilla attacks from anywhere, and it became a full-blown guerrilla war.
The Mujahideens were very familiar with the terrain, while the USSR army faced significant difficulties. Although the USSR had an advantage in airpower, the US provided the Mujahideens with the latest weapon, the Stinger surface-to-air missile, which enabled them to destroy USSR airplanes from the surface. This significantly weakened the USSR’s military power and contributed to their defeat. The USSR fought for ten years in Afghanistan, but in 1988, they began withdrawing their forces, and by February 15th, 1989, all their troops had left. This was a humiliating defeat for the USSR, and the question of who would govern Afghanistan now remained.
As previously mentioned, the Mujahideen were not a singular entity but rather comprised of various groups and clans scattered across Afghanistan. These groups began fighting amongst themselves to establish dominance over the region. In 1992, leaders of several small groups convened in Peshawar, Pakistan to discuss power-sharing arrangements for Afghanistan and its responsibilities. They signed an agreement, known as the Peshawar Accord, to formalize their decision.
However, the Accord faced numerous challenges as some members who received less power refused to uphold their end of the bargain. Consequently, civil war broke out, leading to widespread destruction, chaos, and lawlessness.
The Rise of Taliban
Among the Mujahideen factions, one group stood out – the Student Wing, comprising religious schools and madrasa scholars. This was the strongest group, dedicated to fighting against the USSR. In Pashto, students are called Talib, and thus the wing was named the Taliban. Its ranks included the renowned and intelligent Mullah Mohammad Omar, who was responsible for causing significant damage to the USSR during combat, although he lost an eye in a bomb explosion, leading to immense respect from his peers.
Mullah Omar rose to become the Taliban’s leader, growing in power until, in 1996, he donned the holy cloak of Prophet Mohammed before 1500 religious leaders, including Osama Bin Laden. This traditional cloak, had not been worn for 250 years, further elevating Mullah Omar’s status as a revered leader in Afghanistan.

Under Mullah Omar’s leadership, the Taliban implemented Sharia Law, which stipulated that women could not leave their homes without a male companion, and banned music, movies, and television. Western education was replaced with religious education, and thieves would have their hands cut off and be executed in the streets. The Taliban also destroyed a 1500-year-old Buddha statue in Bamiyan, a UNESCO world heritage site, to eliminate a symbol of a religion other than Islam.
The Taliban’s policies isolated Afghanistan from the world, with only Pakistan, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia recognizing it. This hindered the country’s development, and Osama Bin Laden turned against the USA due to various reasons, such as US military intervention in Saudi Arabia and stopping his operations in Sudan.
Osama had good relations with Mullah Omar, who gave him refuge after he was thrown out of Sudan, and together, they began waging war against terrorists. However, after planning the 9/11 attacks from Afghanistan, the US demanded that the Taliban hand over Osama and eradicate the Al-Qaeda network. Mullah Omar refused, citing several reasons.
Firstly, Osama Bin Laden provided significant support to Mullah Omar during his fight against the USSR. Secondly, this action would have sent a message throughout Afghanistan that the Taliban had surrendered to the US, resulting in a reduction in local support. Furthermore, there is a Pashto saying that one should never hand over their guest to others, and since Osama Bin Laden was considered a guest of Afghanistan, the Taliban could not turn him over.
The Taliban even asked the US to provide proof against Osama Bin Laden, but the request was denied. As a result, Afghanistan did not comply with the US’s demands.
Read More – Korean Peninsula: A Story of Divisions, Diplomacy & Danger
US Invasion
On September 11, 2001, the US was attacked, prompting them to initiate action. The US immediately engaged in talks with the Taliban, but an agreement could not be reached, leading to an attack by the US and its allies – the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and others – on October 7, 2001, as part of Operation Enduring Freedom.
Initially, the US conducted airstrikes against major Al-Qaeda and Taliban locations, but they did not deploy soldiers on the ground or deliver supplies. After a few days, the airstrikes were halted, and the US and its allies sent special forces into Afghanistan, including the Delta Force and Navy Seals of the US Army, as well as the British SAS. On November 9, 2001, they captured the major city of Mazar-i-Sharif, and on November 13, 2001, the Taliban government was removed from power. In the following month, the US took control of the majority of Afghanistan, including Kandahar. Mullah Omar, Osama Bin Laden, and other remaining Taliban leaders hid in Afghanistan. Despite the Taliban’s unsurrendered presence, the US claimed victory.
The US’s primary objective was to find and capture Osama Bin Laden, but he remained out of reach. In December 2001, the US established a government in Afghanistan, and proper elections were held. Hamid Karzai won the presidency with 55.4% of the vote, but the Taliban was excluded from the process. This decision was criticized worldwide, as the Taliban was also considered Afghan citizens. The US invasion of Iraq in 2003 divided its focus, and Osama Bin Laden remained at large.
As soon as US focuses towards IRAQ Taliban starts uniting again. There’s a western Northern region of Pakistan which is called Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA), Taliban meets here again and starts preparing against US. Mullah Omar, who been hiding for quite a while his statement starts coming to light as well and with Haqqani Network, Islamic, Movement of Uzbekistan (IMU) and Al-Qaeda they formed an alliance started preparing quickly against US.
On the contrary, the US-backed government in Afghanistan was plagued by corruption. Officials in the government were more interested in lining their pockets than actually working towards the country’s development. The Taliban capitalized on this sentiment and effectively spread the message among the local population, leading to widespread disillusionment and anger towards the government. As a result, the Taliban was able to gradually regain control of various regions of Afghanistan.
Some may wonder why the US did not intervene and stop the Taliban’s advances. However, it is important to note that at the time, the focus of the US military was primarily on Iraq. The troop levels in Afghanistan were not sufficient to effectively combat the Taliban’s resurgence.
The reason why the Taliban was able to capture many regions of Afghanistan was that the US army was only providing security to the main city. As a result, the government of Afghanistan had to establish a parallel government to address the issues in those areas. Moreover, the Afghanistan-Pakistan border was not properly secured, which made it easy for the Taliban to flee to Pakistan and escape US attacks.
However, the US eventually realized that it needed the help of its allies, such as the UK, Australia, Canada, and the Netherlands, to hang on to Afghanistan for a long time. These countries sent their armies to different provinces of Afghanistan. The Canadian army was sent to Kandahar, while the UK army was sent to Helmand.
Critics From around the World
Despite the efforts of the US and its allies to take control of Afghanistan, mistakes were made, and the citizens of Afghanistan started turning against them. There were many instances where US army personnel killed innocent civilians. For example, in May 2006, a US Army truck caused the death of an Afghan citizen, leading to protests where the US Army killed 20 more civilians. In March 2007, the US army attacked Taliban in Shinwar, and civilians were shot dead. In September 2009, NATO started an air strike in response to the hijacking of two fuel tankers by the Taliban, killing 179 people, including over 100 civilians. The German government had to pay $500,000 in compensation to the families of the victims. In 2008, the US mistakenly bombed a wedding in Haska, killing 47 civilians, including the bride.

(Photo: Peter Macdiarmid/Getty Images)
The leak of more than 90,000 documents related to the Afghan war by Wikileaks in July 2010 further damaged the reputation of the US and its involvement in Afghanistan. These documents revealed how NATO killed civilians and tried to cover up their actions with lies. As a result, the international community criticized the US’s involvement in Afghanistan.
In light of these events, the people of Afghanistan began to feel that the US army had no regard for Afghan culture or its people. As these incidents escalated, even members of the Afghan military began to turn against the US. The local population was filled with animosity towards the US, which made the US army increasingly vulnerable to attack.
The world was left wondering why the US and its allies were still present in Afghanistan. They had initially gone there to capture Osama bin Laden and fight the Taliban, which was not their war. While the US had a legitimate reason to fight in Afghanistan, people questioned why they also attacked Iraq. Although the strategy was in motion, with Osama out of the US radar, the raid on the Abbottabad compound in Pakistan on May 2, 2011, marked a significant victory for the US as they had achieved their objective. However, their fight against the Taliban continued for several years after Osama’s death.
The Withdrawal
Eventually, the US and its allies realized that the Taliban was beyond their control, leading them to adopt a new strategy. Instead of deploying their own soldiers, the Afghan security forces were trained and sent into action, and NATO allies slowly began withdrawing their troops.
Firstly, in July 2011, Canada withdrew from Afghanistan, and the other NATO countries started reducing their troops. In October 2014, the United States and Britain stopped their joint operation in Afghanistan. This meant that any future operation in Afghanistan would not be led by the US and UK, and they would only provide support to Afghan security forces in US operations.
As all these events were unfolding, 2020 brought another significant development when US President Donald Trump offered to talk with the Taliban. On February 29, 2020, an agreement was signed in Doha between the Taliban and the US. However, the government of Afghanistan was kept out of the agreement, which was only between the US and the Taliban. The key point of this agreement was that NATO would completely withdraw from Afghanistan and take back its forces. The Taliban agreed not to support Al-Qaeda or allow them to use their land.
This agreement is also known as the Doha agreement, but some parts of it were kept secret and not made public. These undisclosed elements were only known to the US and the Taliban, and the Afghanistan government was not informed. In the future, the Afghanistan government claimed that the US and the Taliban had planned something against them that would harm them.
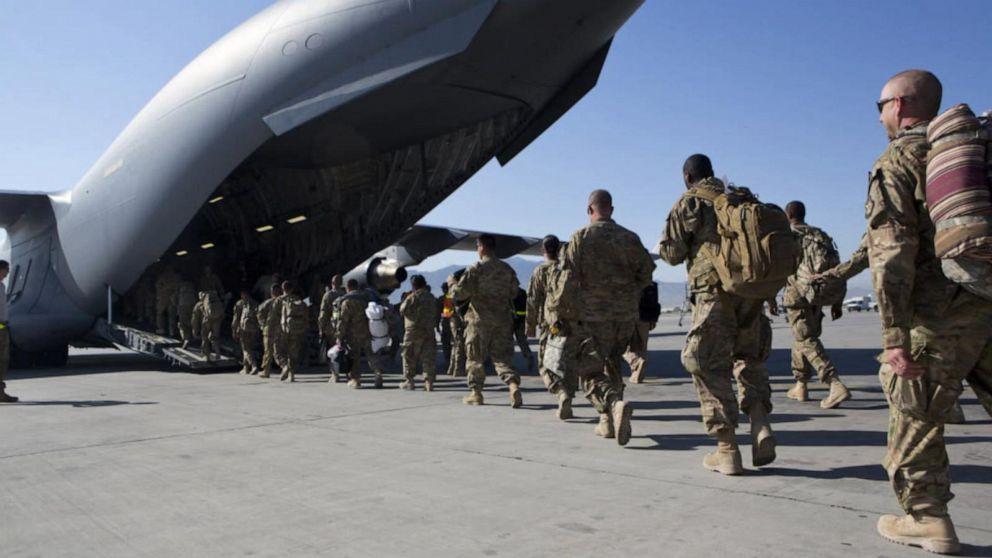

After the signing of the Doha agreement, the US Army started withdrawing from Afghanistan, and in August 2021, they left Afghanistan entirely. During this time, Afghanistan’s President Ashraf Ghani fled the country, causing fear and uncertainty among the Afghan people. They were worried that the Taliban would not spare them, especially those who were on the US’s side or were working with them against the Taliban.
On September 7, 2021, the Taliban removed the Afghanistan government and announced its new government. Mullah Mohammad Hasan announced himself as the PM, and Abdul Ghani Baradar became the Deputy PM. The Taliban claimed that they would give all rights to women, not kill anyone, and not enforce strict laws. However, they have been diverging from their promises. In September 2021, the Taliban said they would continue to give education to females, but after a month, they banned girls from attending secondary schools. In December 2022, the Taliban banned higher education for females.
Another issue in Afghanistan is the $7 billion of Afghan government funds frozen in US banks. The US has refused to return the funds, leading to a severe economic crisis in Afghanistan. More than 20 million people are unable to access proper food, and around 7 million people are at the brink of starvation.
Since 2021, the Taliban has not been recognized by any country, and most countries have stated that they will only recognize the Taliban government if it forms an inclusive government and guarantees the rights of women and minorities.
The current situation in Afghanistan is dire, and the humanitarian crisis is escalating. Approximately 28 million people in Afghanistan will need assistance in 2023 to survive. If the situation is not handled well, it may lead to the Taliban reuniting with Al-Qaeda, which could bring a crisis for the entire world.











1 Comment. Leave new
[…] Also Read: Afghanistan Unveiled – The USSR, USA and Critics […]